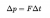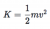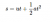If I have made an error, please correct me.
I would say that you should
tick only the second box (ie.
The hovercraft reached a speed of approximately 30m/s)
This is the graph that we were given:
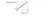
As you may remember, Impulse is the change in momentum:
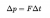
This is basically the area under the graph, which is
(30 x 10)/2 {ie. Area of triangle}
Therefore,
Impulse = 150 kgm/s
As mentioned before, Impulse is the change in momentum (v is final velocity and u is initial velocity):
150 = mv - mu = (5 x v) - (5 x 0)
Therefore, 150 = 5v
and so,
v=30m/s
Now, the other options
shouldn't be selected as:
- The acceleration changes over time - as the force experienced by the hovercraft changes with respect to time and F=ma (where m is 5kg), therefore the acceleration is not constant, the acceleration is only 3m/s^2 when t=10 seconds.
- The hovercraft didn't increase in KE by 150 J
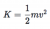
KE actually increases by 2250 J
- The hovercraft didn't travel 5m, if you use this kinematics equation:
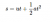
The distance travelled by the hovercraft is actually 150m.